Adaptive Reality Future of Digital Marketing and Game Development
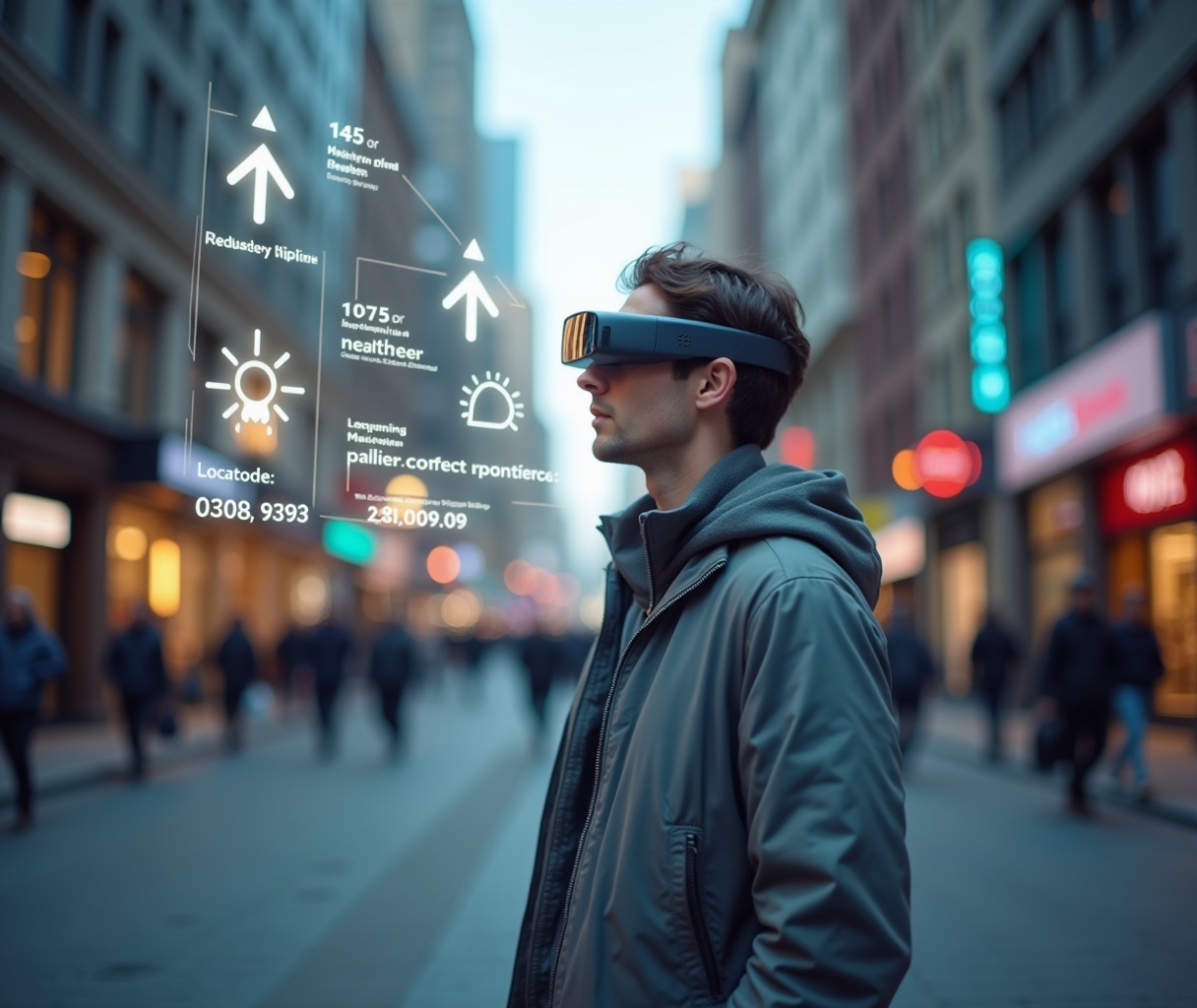
Today’s hyper connected world, the demand for personalized and immersive experiences is driving innovation at lightning speed. One of the most exciting technologies leading this wave is #AR a powerful fusion of real world context, artificial intelligence, and interactive digital overlays that respond dynamically to user behavior, environment, and intent.
AR (AR) goes beyond traditional Augmented Reality (AR) by adapting content and interaction based on real time inputs, such as a user’s location, preferences, device capabilities, and even emotional state. As industries embrace digital transformation, Adaptive Reality is playing a critical role especially in digital marketing and game development by making experiences more relevant, engaging, and personalized.
What Is Adaptive Reality?
AdaptiveReality is an advanced form of augmented reality that dynamically adjusts digital content in response to contextual data. It integrates:
- #AugmentedReality (AR)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Real time environment sensing (via sensors, GPS, cameras)
- User behavior analytics
This blend enables the system to “adapt” based on the individual user’s actions or surroundings offering context aware experiences that traditional AR or static apps cannot.
The Role of AR in Digital Marketing
Hyper Personalized Brand Interactions
Marketers are using AR to create campaigns that react to users’ real world environments. Imagine a customer pointing their phone at a product shelf and seeing dynamically generated content discounts, personalized ads, or even AI driven recommendations.
Real Time Product Visualization
Retailers allow customers to “try on” clothing, makeup, or furniture in real time with Adaptive Reality. The technology adjusts lighting, positioning, and proportions to reflect real world environments, increasing purchase confidence.
3. Event and Location Based Engagement
AR can tailor digital marketing content based on GPS or event participation. For example, a user walking past a billboard might receive a customized promotional video related to the store they’re near, in the language they prefer.
4. Immersive Storytelling
Brands use Adaptive Reality to place consumers inside interactive stories. Think of interactive ads where the user’s environment affects the narrative turning marketing into an engaging game like experience.
The Role of AR in Game Development
Real World Immersion in Game play
Adaptive Reality allows games to blend with the player’s environment, creating truly immersive experiences. The game adjusts challenges, visuals, and interactions based on the player’s location, time of day, weather, and even facial expression.
Enhanced Mobile AR Games
Games like Pokémon Go laid the foundation. Now, Adaptive Reality takes it further if a player is running, the game might increase pace or spawn location based events. If a friend joins nearby, the game could adapt into multiplayer mode in real time.
Dynamic AI Driven NPCs and Environments
Characters and surroundings in games can react to a player’s real world behavior. For example, a character may change dialogue based on your real world calendar, weather, or voice tone, adding a level of realism previously unseen.
Gamification in Non Gaming Contexts
Education, healthcare, and training apps are integrating AR to gamily real world tasks. A language-learning game could adapt questions based on your current mood or concentration level, creating more effective learning loops.
FAQs About Adaptive reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content on the physical world. Adaptive Reality (AR) takes it further by making that content responsive to the user’s real-time context location, behavior, device, environment, and more offering a tailored, intelligent experience.
Brands use AR to deliver personalized ads, interactive try-on experiences, dynamic product visualizations, and location-based promotions. These campaigns react in real time to user data and surroundings, boosting engagement and conversion rates.
Games that change based on weather, physical location, player actions, or nearby users are examples of AR in action. For instance, a zombie survival game might become more difficult at night or introduce multiplayer features when others are nearby.
Adaptive Reality is powered by a combination of AI, AR toolkits (like ARKit, ARCore, or Vuforia), sensors (GPS, gyroscope, camera, microphone), machine learning models, and real-time data analysis frameworks.
While AR development requires a skilled team and access to sensor data and machine learning infrastructure, scalable solutions now exist. Costs depend on complexity, but many businesses start with lightweight AR features and scale over time.